Find a Provider
From well-child visits to specialized treatment of complex illnesses and injuries, we offer comprehensive care from an exceptional team of doctors, nurses and allied professionals.
- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Strep Throat
What Is Strep Throat?
Strep throat is an infection caused by a type of bacteria called group A strep (or GAS).
Strep throat usually requires a trip to the doctor and treatment with antibiotics. With the proper medical care — along with plenty of rest and fluids — you should feel better in no time.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Strep Throat?
Most sore throats are caused by viruses. If you have a runny nose, cough, hoarseness, and red or runny eyes, it's probably a virus and will clear up on its own.
Strep throat is different. Signs that you may have strep throat include:
- sore throat that comes on quickly and is especially painful when swallowing
- a fever
- red and swollen tonsils with white patches or streaks on them
- painful or swollen neck glands (lymph nodes)
If you have any of these symptoms, it's definitely time to see your doctor.
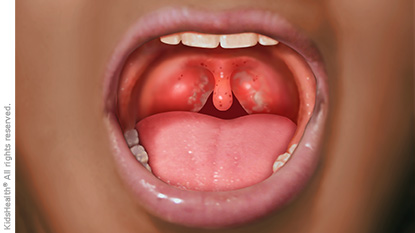
Is Strep Throat Contagious?
Strep throat is very contagious. Anybody can get it, but most cases are in school-age kids and teens ages 5 to 15. Infections are common during the school year, with peaks in winter and early spring, when big groups of students are in close contact.
How Do People Get Strep Throat?
The bacteria that cause strep throat tend to hang out in the nose and throat. So normal activities like talking, sneezing, coughing, or shaking hands can easily spread an infection from one person to another. People also can get infected if they touch a surface with the bacteria on it, then touch their nose or mouth.
People with untreated strep throat are more likely to spread the infection when their symptoms are most severe, but can still infect others for up to 3 weeks.
After they get infected, people can spread the bacteria to others for a few days before they have any symptoms. That's why it's so important to wash your hands well and often. This can lower your chances of getting contagious diseases like strep throat.
How Is Strep Throat Diagnosed?
Doctors might do a rapid strep test right in the office. They'll use a swab to take a sample of the fluids at the back of your throat. It usually only takes a few minutes to find out if you've got strep throat.
If the first test doesn't prove anything, then your doctor might do a longer swab test called a throat culture. The results are usually available within a couple of days.
How Is Strep Throat Treated?
Doctors usually prescribe 10 days of antibiotic medicine to treat strep throat. Even though strep throat can go away on its own after about a week, antibiotics can help make a person feel better faster and can keep the infection from spreading to other people.
Within about 12 hours after starting on antibiotics, you probably won't have a fever and won't be contagious. By the second or third day, other symptoms should start to go away. Most teens can go back to school when they've taken antibiotics for at least 12 hours and no longer have a fever.
Even when you feel better, keep taking the antibiotics as prescribed. This is the best way to kill the harmful bacteria. Otherwise, bacteria can stay in the throat and symptoms can come back. Taking all the antibiotics also prevents other health problems that GAS can cause, such as rheumatic fever (which can cause heart damage), kidney disease, or more serious infections in other parts of the body.
Can Strep Throat Be Prevented?
If someone in your house has strep throat, follow these tips to help protect yourself from getting it:
- The person with strep throat should cover their mouth when sneezing and coughing. If they don't have a tissue handy, they should cough or sneeze into their elbow — not their hands!
- Don't touch used tissues or other germy items.
- Wash your hands well and often, especially before eating.
- Don't share food, drinks, napkins, handkerchiefs, or towels.
- Wash dishes, drinking glasses, knives, forks, and spoons in hot, soapy water.
If you're the one who's sick, use new toothbrush after you start taking the antibiotics and are no longer contagious.
How Can I Feel Better?
Drink lots of cool liquids, especially if you have a fever, so you don't get dehydrated. Stay away from orange juice, lemonade, and other acidic drinks because they can sting your throat. Frozen foods such as ice cream or popsicles can help to numb throat soreness. Warm liquids like soups, tea with honey, or hot chocolate also can be soothing.
For fever and pain, your doctor may suggest an over-the-counter medicine, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Follow the package directions on how much to take and when.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.


