- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Jumper's Knee
What Is Jumper's Knee?
Jumper's knee is an injury of the patellar tendon. The patellar tendon is the cord-like tissue that joins the patella (kneecap) to the tibia (shinbone).
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Jumper's Knee?
Common symptoms of jumper's knee include:
- pain below the kneecap, especially during sports, climbing stairs, and bending the knee
- a swollen knee joint
- knee stiffness
What Causes Jumper's Knee?
Jumper's knee is an overuse injury (when repeated movements injure a part of the body). It happens when frequent jumping, running, and changing direction damages the patellar tendon. It's also called patellar tendonitis.
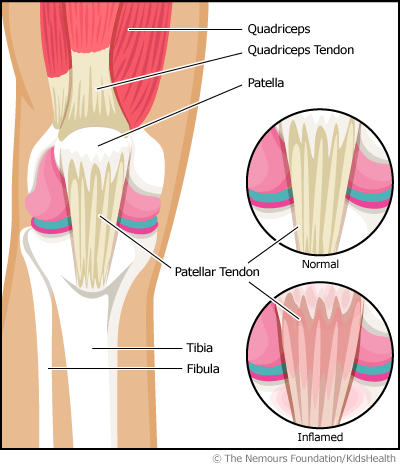
Who Gets Jumper's Knee?
Jumper's knee usually affects people who play sports where there is a lot of jumping and running, such as track and field, basketball, volleyball, gymnastics, running, and soccer.
How Is Jumper's Knee Diagnosed?
To diagnose jumper's knee, health care providers:
- ask about symptoms
- do a physical exam
- order imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI, if needed
How Is Jumper's Knee Treated?
Treatment for jumper's knee includes:
- rest and taking a break from sports
- ice
- taping or wearing a knee support or strap just under the patella
- sitting with the leg raised
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, or store brand) to help with pain and swelling
- massage therapy
- strengthening and stretching muscles through physical therapy or an at-home exercise program
If someone with jumper's knee does not rest the knee, the tendon can become more damaged. Although it is not common, surgery may be needed if:
- the pain does not go away
- the patellar tendon is more damaged than is typical with jumper's knee
Looking Ahead
It usually takes a few weeks to months to recover from jumper's knee.
To heal as quickly as possible, follow your health care provider's instructions about:
- which activities to avoid
- which activities are OK (for example, swimming may be fine while you heal)
- strengthening exercises
- making and keeping all follow-up doctor visits
After recovery, always stretch before and after sports, and avoid overtraining. This can help prevent jumper's knee and other sports injuries too.
- Meniscus Tears
- Sports and Exercise Safety
- Choosing the Right Sport for You
- Overuse Injuries
- Sports Medicine (Topic Center)
- Basketball Safety Tips
- Knee Injuries
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease
- Soccer Safety Tips
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears
- 5 Ways to Prepare for Your Sports Season
- Bursitis

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.