Corporate Circle Members
40 Exchange Place, Suite 1902, New York, NY 10005
Phone
917.746.8300
Members Only
877.662.7627
© 2020 NAPNAP, Inc. All rights Reserved
Growth plates are the areas of new bone growth in children and teens. They're made up of , a rubbery, flexible material (the nose, for instance, is made of cartilage).
Most growth plates are near the ends of long bones. Long bones are bones that are longer than they are wide. They include:
Growth plates are one way bones grow. There are usually two growth plates in each long bone. They add length and width to the bone.
As kids grow, the growth plates harden into solid bone. A growth plate that has completely hardened into solid bone is a closed growth plate. After a growth plate closes, the bones are no longer growing.
Growth plates usually close near the end of puberty. For girls, this usually is when they're 13–15; for boys, it's when they're 15–17.
The growth plate is weaker than solid bone. This makes it more likely to get injured.
These problems can happen with growth plates:
Growth plate fractures are when there is a break in the growth plate. This happens most often in the bones of the fingers, forearm, and lower leg. Most growth plate fractures heal and do not affect future bone growth.
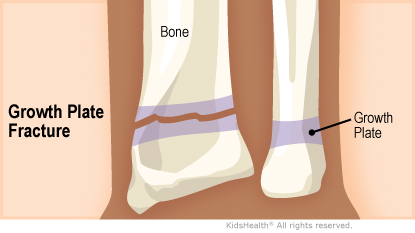
Sometimes, changes in the growth plate from the fracture can cause problems later. For example, the bone could end up a little crooked or a bit longer or shorter than expected.
Overuse injuries (also called repetitive stress injuries) can affect the growth plate in kids and teens. Overuse injuries happens from repeating the same movement over and over. They usually happen to people who play sports.
Overuse injuries that involve the growth plate include:

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
New UsersCreate a User AccountBecome a Member |
Forgot PasswordForgot your password? Click here |
