- Home
- Parents Home
- Allergy Center
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- A to Z Dictionary
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Food Allergy Center
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Flu Center
- Heart Health
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Diseases & Conditions
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Play & Learn Center
- School & Family Life
- Pregnancy Center
- Newborn Center
- Q&A
- Recipes
- Sports Medicine Center
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Videos
- Para Padres
- Home
- Kids Home
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Movies & More
- Diabetes Center
- Getting Help
- Feelings
- Puberty & Growing Up
- Health Problems of Grown-Ups
- Health Problems
- Homework Center
- How the Body Works
- Illnesses & Injuries
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes & Cooking
- Staying Healthy
- Stay Safe Center
- Relax & Unwind Center
- Q&A
- Heart Center
- Videos
- Staying Safe
- Kids' Medical Dictionary
- Para Niños
- Home
- Teens Home
- Asthma Center
- Be Your Best Self Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Expert Answers (Q&A)
- Flu Center
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Managing Your Medical Care
- Managing Your Weight
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes
- Safety & First Aid
- School & Work
- Sexual Health
- Sports Center
- Stress & Coping Center
- Videos
- Your Body
- Your Mind
- Para Adolescentes
Pinkeye (Conjunctivitis)
What Is Pinkeye?
You might know the eye infection conjunctivitis (pronounced: kun-junk-tih-VY-tus) as pinkeye. It's common in young kids because it's usually contagious and tends to sweep through preschools and playgrounds. But even teens and adults can get pinkeye.
The good news is that pinkeye is a minor infection and although it might look bad, it's not usually serious.
What Causes Pinkeye?
Pinkeye is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the white part of the eye and the inner eyelids. The condition can be either infectious (it can spread to other people) or noninfectious.
When people talk about pinkeye, they usually mean the infectious kind. It's often caused by the same bacteria and viruses responsible for colds and other infections, including ear infections, sinus infections, and sore throats.
It's also possible for the same types of bacteria that cause the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)chlamydia and gonorrhea to cause conjunctivitis. If someone touches an infected person's genitals and then rubs his or her own eye or touches a contact lens, the infection can spread to the eye.
Some kinds of pinkeye are noninfectious, such as:
- allergic conjunctivitis, caused by an allergic reaction
- irritant conjunctivitis, caused by anything that irritates the eyes, such as air pollution or chlorine in pools
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Pinkeye?
The very pink or red coloring that gives the infection its nickname is a telltale sign of pinkeye. It's also usual to have discomfort in the eye, which may feel itchy or gritty. Often, there's some discharge from the eye, and pain and swelling of the conjunctiva. Pinkeye can affect one or both eyes.
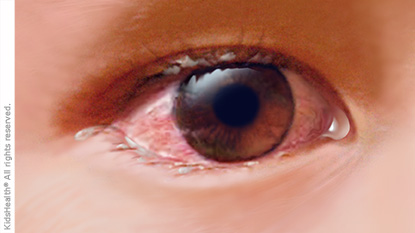
It can be hard to tell whether the infection is caused by a virus or bacteria. In general, the discharge associated with viral conjunctivitis is watery, whereas it will be thicker and more pus-like when the infection is caused by bacteria. When you wake up in the morning, your eyelids may be stuck together (don't be alarmed, though — cleaning your eyes with a warm washcloth will loosen the dried crusts).
Itchiness and tearing are common with allergic conjunctivitis.
Is Pinkeye Contagious?
Yes, if it's caused by bacteria or a virus. Pinkeye that's caused by bacteria can spread to others as soon as symptoms appear and for as long as there's discharge from the eye — or until 24 hours after antibiotics are started. Conjunctivitis that's caused by a virus is generally contagious before symptoms appear and can remain so as long as the symptoms last.
Allergic conjunctivitis and irritant conjunctivitis are not contagious.
How Is Pinkeye Treated?
Because it can be hard to tell which kind of conjunctivitis a person has, it's wise to visit a doctor if your eyes are red and irritated.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is usually treated with prescription antibiotic drops or ointment. Drops — the form of treatment most commonly prescribed for teens — are used up to four times a day. They don't hurt, although they may cause a brief stinging sensation. Even though your eyes should feel and look better after a couple of days, it's important to use the drops for as long as the doctor has prescribed. The infection may come back if you stop too soon.
If a virus is causing conjunctivitis, antibiotic drops will not help. The eye infection will get better on its own as the body fights off the virus.
If you have allergic conjunctivitis, your doctor may prescribe anti-allergy eyedrops or medicine in pill form.
Can Pinkeye Be Prevented?
Because infectious conjunctivitis is highly contagious, wash your hands after interacting with anyone who has the infection. Don't share potentially infected items like washcloths, towels, gauze, or cotton balls. This can be difficult among family members, so just do the best you can.
If you have pinkeye, it's important to wash your hands often, especially after touching your eyes. The infection can easily spread from one eye to the other on contaminated hands or tissues.
It's also wise not to share cosmetics, especially eye makeup. Bacteria can hang out on beauty products, so avoid using the testers at makeup counters directly on your eyes. And if you've already had a bout of pinkeye, throw away all your eye makeup and splurge on new stuff (but don't start using your new products until the infection is completely gone).
If you wear contact lenses and you have pinkeye, your doctor or eye doctor may recommend that you not wear contact lenses while infected. After the infection is gone, clean your lenses carefully. Be sure to disinfect the lenses and case at least twice before wearing them again. If you wear disposable contact lenses, throw away your current pair and use a new pair.
If you know that you're prone to allergic conjunctivitis, limit allergy triggers in the home by keeping windows and doors closed on days when pollen is heavy and by not letting dust accumulate. Irritant conjunctivitis can only be prevented by avoiding the irritating causes.
How Can I Feel Better?
Placing cool or warm packs or washcloths over the infected eye (or eyes) can help. You can also take acetaminophen, if necessary. Clean the infected eye carefully with warm water and fresh, clean gauze or cotton balls.
Keep track of your symptoms, keep your hands clean, visit your doctor as needed, and follow your treatment instructions carefully. Within a week, your eyes should be feeling better.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.