Pregnancy at 2 Weeks: Weekly Calendar
What’s Happening in My Body?
Am I Pregnant?
This may sound strange, but you're not pregnant yet! Fertilization of your egg by the sperm will take place near the end of this week. The reason that you're considered 2 weeks pregnant is that doctors start calculating your pregnancy based on the first date of your last menstrual period.
Conception at 2 Weeks
Your uterine lining (which will nourish your baby) is developing and your body secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) which stimulates an egg to mature. At the end of this week, you will be at the midpoint of your menstrual cycle (if you have a regular 28-day cycle). Ovulation happens when the ovary releases an egg into the fallopian tube.
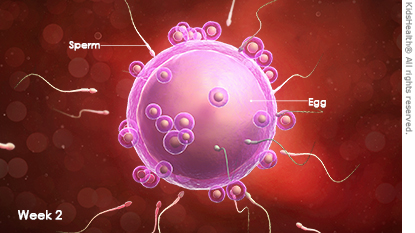
This week is when you're most likely to conceive. If you have sex around the time that you ovulate, you can become pregnant. After the male ejaculates, millions of sperm travel through the vagina, and hundreds make it to the fallopian tube, where the egg is waiting. One sperm generally succeeds in penetrating the egg, and fertilization takes place. When that happens, you will be pregnant — but you won't feel any body changes just yet.
When Will I Know My Baby’s Gender?
The sex of your baby is determined at the moment of fertilization. Out of the 46 chromosomes that make up a baby's genetic material, only two — one from the sperm and one from the egg — determine your baby's sex. These are known as the sex chromosomes. Every egg has an X sex chromosome; a sperm can have either an X or a Y sex chromosome. If the sperm that fertilizes an egg has an X chromosome, the baby is female; if it has a Y chromosome, the baby will be a boy.
However, you’ll have to be patient! If you choose to learn your baby’s gender, you will most likely need to wait until 18 to 20 weeks into your pregnancy when your doctor can tell the gender from an ultrasound.
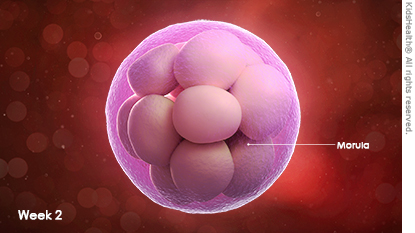
How Will I Know That I’m Pregnant?
A missed period is typically the first sign of pregnancy, but some women feel pain or cramping around day 5 or 6 after sex (when the fertilized egg implants in your uterus). Within the next few weeks, you may have early signs of pregnancy like fatigue, breast tenderness, or cramping.
After missing a period, many women choose to take an at-home pregnancy test to confirm it before calling the doctor to set up a first prenatal visit.
Important Appointments to Schedule
Although your pregnancy has not happened yet, if you are trying to conceive, it’s a good idea to make an appointment with your primary care doctor to ensure you’re prepared for a healthy pregnancy. It’s a good opportunity to ask any questions or share concerns you have around pregnancy in general. When you see the doctor, you should ask about any prescription, over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, or supplements you are taking, to ensure they are safe in pregnancy. Also, make sure you are taking your prenatal vitamins (with folic acid).
You will want to schedule your first obstetrics appointment between 6 and 10 weeks of pregnancy. Obstetrics is medical care before and during pregnancy, childbirth, and right after a baby is born.
If you do not have an obstetrician, this is a good time to find one. Ask your primary care doctor for names of doctors and you can ask friends and family who have recently given birth for their recommendations.
When to Get Prenatal Care Earlier
Going regularly for prenatal care helps you and your baby stay healthy. It also lets doctors find and deal with any problems as soon as possible.
If your pregnancy is considered high risk (for example, if you are older than age 35 or have a history of pregnancy complications), your doctor may want to see you as early as possible and more often during your pregnancy.


 Note: All information is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice,
diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.
Note: All information is for educational purposes only. For specific medical advice,
diagnoses, and treatment, consult your doctor.