- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Thyroid Tests
What Is the Thyroid?
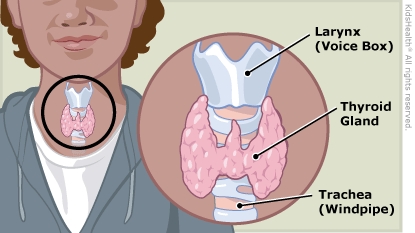
The thyroid is a small gland below the skin and muscles at the front of the neck, at the spot where a bow tie would rest. It makes two types of thyroid hormones: T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). It helps the body do many things, such as get energy from food, grow, and go through sexual development.
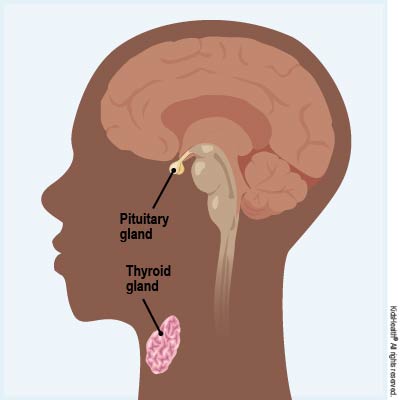
The pituitary is a pea-sized gland at the bottom of the brain that makes thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH triggers the thyroid to make more thyroid hormone. The pituitary gland and the thyroid gland send messages back and forth to each other about how much hormone to make to keep the levels normal.
What Is Thyroid Disease?
Some diseases of the thyroid or pituitary gland cause the thyroid to make too much or not enough thyroid hormone:
- If the thyroid is overactive, it releases too much thyroid hormone, causing hyperthyroidism. The body use up energy more quickly than it should, and chemical activity (like metabolism) in the cells speeds up. Symptoms may include sweating, trembling, weight loss, and fast heartbeat.
- If the thyroid is underactive, it makes too little thyroid hormone, causing hypothyroidism. The body uses up energy more slowly, and chemical activity (metabolism) in the cells slows down. Symptoms may include tiredness, feeling cold, constipation, dry skin, and slow height growth in children.
- Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can make the thyroid larger than normal. An enlarged thyroid gland can be felt under the skin at the front of the neck. When it is large enough to see easily, it's called a goiter. A thyroid nodule is a lump or enlarged area in the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid cancer is uncommon in children. When it does happen, the results of treatment are usually excellent.
What Are Thyroid Blood Tests?
Doctors use blood tests to check for thyroid or pituitary problems. In kids already diagnosed with thyroid or pituitary problems, the tests are used to guide treatment.
Commonly ordered thyroid blood tests include:
- T4 test: This is done to measure the blood level of the hormone T4 (thyroxine). It might be done in one or both of the following ways:
- total T4, which measures the entire amount of thyroxine in the blood, including the amount attached to blood proteins that help carry the hormone through the bloodstream
- free T4, which measures only the thyroxine that's not attached to proteins. This is the part of T4 in the blood that affects how the body's cells work.
The results of the T4 blood tests can help diagnose hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism and guide treatment.
- TSH test: A thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test can help tell how well the thyroid is working. If a thyroid disease prevents the gland from making enough thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland releases more TSH into the blood. If the thyroid is making too much thyroid hormone, the pituitary releases less TSH, which can lower the levels of TSH in the blood.
- T3 total test: The T3 total test measures the other major thyroid hormone in the blood. It often helps doctors diagnose hyperthyroidism.
- thyroid antibodies test: Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an condition in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. To diagnose it, doctors check for high levels of antibodies that are a sign of the immune system's attack on proteins in the thyroid gland. Usually, two types of thyroid antibodies are measured: thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb) and thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO).
In some cases, abnormal thyroid test results can be due to a medicine, an ongoing medical condition, or pregnancy. In these cases, there may be nothing wrong with the thyroid or pituitary glands themselves.
The normal ranges of thyroid function test results vary by age. Doctors think about this carefully when they interpret them.
What if I Have Questions?
If you have any questions about a thyroid blood test or what the results of the test mean, talk with your child’s doctor.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
