- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
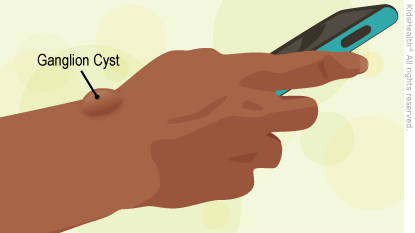
Ganglion Cysts
What Are Ganglion Cysts?
Ganglion cysts are lumps that, most commonly, develop on the back of the wrist. Underneath the skin is a fluid-filled sac.
Although they're known medically as soft tissue tumors, ganglion (GAN-glee-in) cysts are not cancerous and are easily treated.
What Causes Ganglion Cysts?
Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglion cysts. They're most common in people 15–40 years old. But people of any age can have a ganglion cyst.
Some ganglion cysts are associated with arthritis.
How Do Ganglion Cysts Develop?
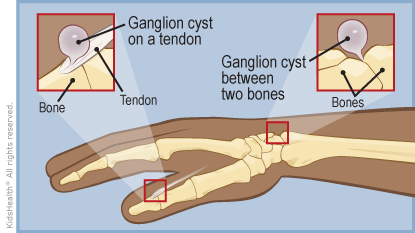
Moving parts have lubrication fluid — in a car, for instance, the engine has motor oil. In the body, joints and tendon sheathes (space around tendons) make synovial fluid (a thick lubrication fluid). This fluid is supposed to stay in the joint or in the tendon sheathe.
A ganglion cyst forms when the joint or tendon sheathe has a "leak." This leak develops a thin wall around it and forms a cyst under the skin.
If you could look beneath the skin to see a ganglion cyst, it would resemble a water balloon (the cyst) attached to a faucet (the joint or the tendon).
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of a Ganglion Cyst?
The distinctive lumps are the main sign of ganglion cysts. Most are round or oval. They might change size, growing larger or smaller as more fluid leaks in or gets absorbed. Most ganglion cysts are not painful, but they may hurt with certain movements. For example, a cyst on the top of the wrist may cause pain when the person does a push-up.
While most ganglion cysts are on the back of the hand or wrist, they sometimes can form on the palm side of the wrist, the base of the finger on the palm side, and the top of the feet.
How Are Ganglion Cysts Diagnosed?
Doctors usually can diagnose a ganglion cyst based on where it is and how it looks and feels. The cyst can be soft or firm.
Ganglion cysts usually will transilluminate (let light through) in an office test using a small light. They also can be easily viewed with an ultrasound.
How Are Ganglion Cysts Treated?
Many ganglion cysts go away without medical treatment. Doctors often decide to "watch and wait" to see if a cyst goes away or doesn't get worse, especially if it's not painful. Most ganglion cysts in children will go away on their own within 1 year.
If repetitive movements make the cyst bigger or more painful, the doctor may recommend rest and wearing a splint or brace. Anti-inflammatory medicines can help ease minor pain or discomfort.
Note: You might have heard a ganglion cyst called a "Bible cyst" or "Bible bump." That's because a common home remedy in the past was hitting the cyst with a Bible or other thick book to try to make the cyst rupture or pop. Doctors don't recommend this treatment. Occasionally a cyst will rupture if a child falls on it. If this happens, the area will be red, swollen, and sore for a few days.
Aspiration
If a cyst is bothersome, painful, or long-lasting, a doctor might "aspirate" (or drain) it with a long needle. In this quick and effective office procedure, a doctor will:
- Numb the area around the ganglion cyst.
- Puncture the cyst with a needle, then withdraw the fluid.
Even with aspiration, a ganglion cyst may come back. That’s because aspiration only removes the fluid in the cyst. It doesn't remove the cyst or its connection to the source of the fluid. (It takes the fluid out of the "water balloon," which is still connected to the "faucet.")
Excision
In some cases, a doctor might recommend a minor surgery to remove a ganglion cyst. The surgical procedure — called a ganglion excision, or ganglionectomy — removes the ganglion cyst along with the stalk.
Home Care After an Excision
If your child has an excision, the area will be covered with a dressing or bandages and usually a splint or cast.
The surgical site might be tender and swollen. Keeping the hand raised above the level of the heart for a few days can help ease swelling. For pain, ask your health care provider about giving your child ibuprofen or acetaminophen. An ice pack wrapped in a towel also can help with pain and swelling. Keep the bandages and splint dry, covering them with a waterproof bag when your child bathes or showers.
At a follow-up visit, the health care provider might recommend physical therapy or occupational therapy to help your child's recovery. Most kids can return to normal activities 2–4 weeks after the surgery.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
