- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Knee Injuries
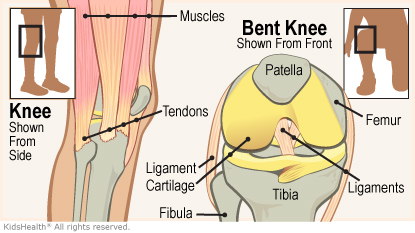
The knee is a joint that joins the thighbone (femur) to the top of the shinbone (tibia). It’s made up of bones; muscles; and tissues called , tendons, and . These parts work together to let the legs bend, straighten, and turn. A knee injury can damage one or more parts of the knee.
What Causes Knee Injuries?
People may hurt a knee in a fall or accident. Others get overuse knee injuries. These happen when someone trains too much for a sport or makes the same motions over and over with the knee.
Common knee injuries include:
- sprains: when a ligament stretches or tears, like with an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL) tear
- strains: when a muscle or tendon stretches too far
- tendonitis:of a tendon that’s often from overuse, like with jumper's knee
- meniscal tears: when the cartilage between the upper and lower leg bones (the menisci) tears
- fractures: when a bone breaks
- dislocated patella (kneecap): when the kneecap slides out of place
- Osgood-Schlatter disease: inflammation of the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shinbone
- osteochondritis dissecans (pronounced: oss-tee-oh-kon-DRITE-iss DISS-ih-kanz): when a small piece of bone in the knee loses blood supply and breaks off
- bursitis: swelling of one of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of a Knee Injury?
Signs and symptoms of a knee injury depend on the cause. Most people with knee injuries have pain. The knee may also feel weak or like it’s "giving way" or "locking." People might not be able to fully bend or straighten the knee, which also might be swollen or bruised.
How Are Knee Injuries Diagnosed?
To diagnose a knee injury, doctors ask how the injury happened and what symptoms it's causing.
They'll do an exam where they press on the knee and legs, and move them in certain ways. This can help show what part of the knee is hurt.
Some people may need imaging tests like an X-ray to check for injuries to the bones, or a CT scan or an MRI to look inside the knee.
How Are Knee Injuries Treated?
Treatment for a knee injury depends on the cause. Follow your doctor’s instructions for what activities are OK. If an activity causes pain, stop doing it. You can try that activity later on or the next day.
If your doctor says it’s OK, you can take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Follow the label directions for how much to take and how often.
To help with swelling in the first day or two after the injury, you can:
- Put ice in a towel on your knee for about 20 minutes every 1 to 2 hours.
- Wrap an elastic bandage around your knee or use a compression sleeve.
- Raise your knee above the level of your heart.
Sometimes, a person with a knee injury may need physical therapy or surgery.
Can Knee Injuries Be Prevented?
To help prevent knee injuries, wear the right protective equipment for sports (like knee pads and shin guards). You also need supportive athletic shoes that are in good condition.
Learn how to move safely. When jumping, bend your knees while landing. And when changing directions or turning quickly (as in soccer), crouch and bend at the knees and hips. This helps lower your chances of an ACL injury.
Be sure to warm up before a workout and cool down after it. You can also do regular strength training to support muscles, and stretching or yoga to be more flexible.
Finally, try to stay active year-round, even if you’re not playing an organized sport. This can help keep your knees and the rest of you in shape.
What Else Should I Know?
If your knee hurts, it’s important to find out why. A visit to your doctor can help you find the cause and get treatment.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
Humana Healthy Horizons in Ohio
- Humana Healthy Horizons
- Humana Healthy Horizons Extras
- Member Support
- Care management
- Caregiver resources
- Child well-being
- Disease management
- Documents and forms
- Enrollment
- Grievances and appeals
- Health and wellness
- KidsHealth
- Member Handbook
- New Member Resources
- News and alerts
- OhioRISE Plan
- Pregnancy outcomes
- Tobacco cessation
- Why Humana
- Your primary care provider
- For Providers
- Contact us
- Accessibility
- Humana Healthy Horizons
- Humana Healthy Horizons Extras
- Member Support
- Care management
- Caregiver resources
- Child well-being
- Disease management
- Documents and forms
- Enrollment
- Grievances and appeals
- Health and wellness
- KidsHealth
- Member Handbook
- New Member Resources
- News and alerts
- OhioRISE Plan
- Pregnancy outcomes
- Tobacco cessation
- Why Humana
- Your primary care provider
- For Providers
- Contact us
- Accessibility