- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Scoliosis
What Is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is when the vertebrae (the small bones in the spine) form a curved line instead of being straight. Sometimes they also rotate (twist), like a corkscrew. This can cause health problems.
Although the spine is sometimes called "the backbone," it's not just one bone. It's made of lots of small bones (called vertebrae) that are connected by a type of elastic tissue called . This gives people the flexibility to bend, stretch, balance, and even walk.
Small curves usually don't cause problems. But a curve that gets worse can be bad for a person's health. Health care providers treat scoliosis (sko-lee-OH-sis) with back braces or surgery when needed.
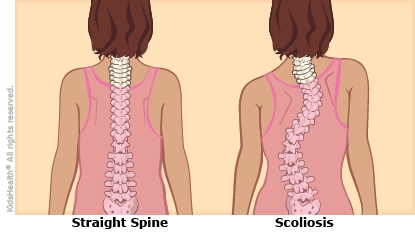
What Are the Types of Scoliosis?
Orthopedic specialists group scoliosis into types. Knowing the type of scoliosis helps them decide how to treat it.
- Idiopathic scoliosis. This is the most common type of scoliosis. Kids can get it at any age, but most of the time it happens around puberty when a child goes through a growth spurt. Experts don't know exactly why this type of scoliosis develops, but it runs in some families.
- Congenital scoliosis. This type of scoliosis happens when something goes wrong with the way some vertebrae developed before a baby was born. The problem might not be noticed until a child goes through a growth spurt, usually around age 2 or between 8 and 13.
- Scoliosis caused by a medical condition. Some kids develop scoliosis because they have a long-term medical problem that affects the muscles or skeletal system. For example, kids with muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, Marfan syndrome, or osteogenesis imperfecta may get scoliosis. Kids who have had tumors or growths on their spine may also develop scoliosis.

Understanding Scoliosis
Find out more about what scoliosis is, who gets it, and what to expect during treatment.
How Is Scoliosis Treated?
Small curves usually don't cause problems. But a curve that gets worse can be bad for a person's health. Very large curves can damage the joints and cause arthritis of the spine. Large curves can make the ribs rub against the pelvis, causing pain. Someone whose spine curves a lot might get lung problems.
Doctors will keep an eye on large curves by doing X-rays. They might decide to treat one with bracing or surgery. The treatment used depends on the type of scoliosis and how much more a child will grow.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.