- Home
- Humana Medicaid
- Kentucky Medicaid
- Medicaid extras
- Health and wellness
- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Gene Changes (Mutations)
What Is a Gene Mutation?
A gene mutation (myoo-TAY-shun) is a change in one or more genes. Some mutations can lead to genetic disorders or illnesses.
What Are Genes?
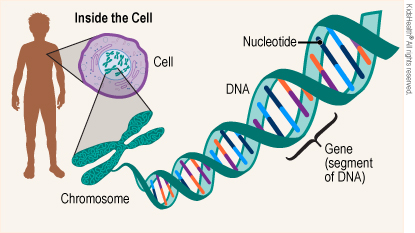
Genes are short sections of DNA. They determine our traits, which are things like hair color, height, body type, and other things that make a person unique. Genes also play a role in a person's risk for some diseases and health conditions. Each of us has about 24,000 different types of genes.
What Is DNA?
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid is the carrier of all our genes. Each person gets one copy of DNA from their mother and one copy from their father. DNA creates a code using four chemicals called nucleotides (NEW-klee-uh-tydes). This code determines which genes a person has. DNA is located inside the chromosomes.
What Is a Chromosome?
A chromosome (KRO-muh-sohm) is an X-shaped thread-like structure in the body's cells. It contains DNA. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
What Causes a Gene Mutation?
A gene can mutate because of:
- a change in one or more nucleotides of DNA
- a change in many genes
- loss of one or more genes
- rearrangement of genes or whole chromosomes
Do Parents Pass Gene Mutations to Children?
If a parent carries a gene mutation in their egg or sperm, it can pass to their child. These hereditary (or inherited) mutations are in almost every cell of the person's body throughout their life. Hereditary mutations include cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease.
Other mutations can happen on their own during a person's life. These are called sporadic, spontaneous, or new mutations. They affect only some cells. Damage from the sun's ultraviolet radiation or exposure to some types of chemicals can lead to new mutations. These mutations are not passed from parents to their children.
Do All Gene Mutations Cause Health Problems?
Most gene mutations have no effect on health. And the body can repair many mutations. Some mutations are even helpful. For example, people can have a mutation that protects them from heart disease or gives them harder bones.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.