- Home
- Humana Medicaid
- Kentucky Medicaid
- Medicaid extras
- Health and wellness
- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
External Fixator: Pin Care
What Is an External Fixator?
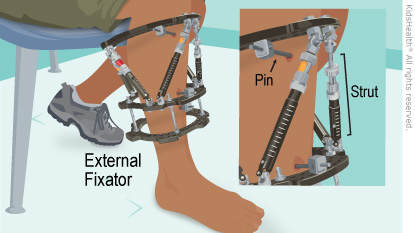
An external fixator is a metal frame that holds bones in place. It has pins that go through the skin and into the bone. The external fixator used for limb lengthening has bars (called struts) that are turned to slowly lengthen and realign the bone.
Why Is Pin Care Important?
The pins go through the skin and into the bone, which can give germs a way to get into the body and cause infections. If an infection happens, your child will need to take antibiotics. Keeping the pins clean helps prevent infection.
How Do I Clean the Pins?
Clean the pins once a day unless your care team gives you other instructions.
If germs from one pin site get onto another pin site, this can cause infection. So don't let anything that touches one pin touch another. This includes gloves, gauze, tweezers, cotton swabs, and anything else that touches the pins.
To clean the pins:
- Wash your hands and put on gloves (the gloves do not need to be sterile).
- Remove any crusting around the pins:
- Wrap sterile gauze soaked with saline around the pin site and let it sit for a few minutes. Use a separate gauze for each pin site.
- When the crusting is softened, remove it with a cotton swab (use a separate swab for each pin site) or tweezers that are cleaned with alcohol on sterile gauze before using and between each pin.
- Remove any clear or yellow drainage with a cotton swab (use a separate swab for each pin site) or tweezers that are cleaned with alcohol on sterile gauze before using and between each pin.
- Use a squeeze bottle to squirt saline on each pin and surrounding skin. Do not touch the tip of the bottle to the pins or skin.
- Dry around each pin using sterile gauze or cotton swabs. Use a clean gauze or swab for each pin.
What Are the Signs of a Pin Infection?
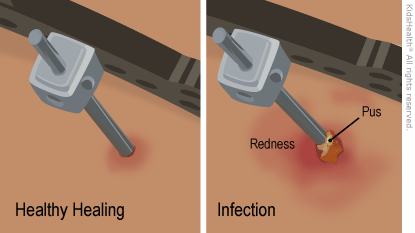
Redness, pain, warmth, swelling, pus or more drainage from any of the pin sites can be signs that your child has a pin infection. A fever higher than 100.4°F (38°C) also can be a sign of a pin infection.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call your surgeon right away if your child has signs of a pin infection. Your child needs antibiotics to make the infection go away.
Looking Ahead
Taking care of an external fixator takes time and patience. Keep a positive attitude that lets your child know that you can do it together. With your help, your child can get the best results from the surgery.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.