- Home
- Humana Medicaid
- Kentucky Medicaid
- Medicaid extras
- Health and wellness
- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
A to Z: Epididymitis
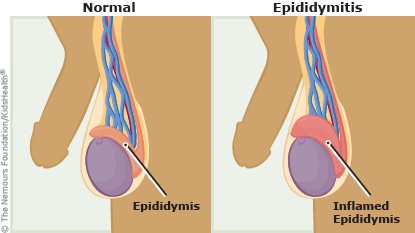
Epididymitis (ep-uh-di-duh-MY-tiss) refers to swelling and inflammation of the epididymis, the coiled tube at the back of the testicle that holds and carries sperm.
More to Know
The most common cause of epididymitis is an infection, sometimes a sexually transmitted disease (STD) (also called sexually transmitted infection or STI) like chlamydia. Urinary tract abnormalities, procedures, and infections also can lead to epididymitis.
Symptoms can include swelling; pain; redness; a heavy sensation of the scrotum; fever; discharge; and pain with urination, defecation, or ejaculation.
In addition to a physical exam, the doctor might have done urine tests, blood tests, an ultrasound or other imaging study, and/or a swab of the urethra in order to diagnose epididymitis.
Keep in Mind
Epididymitis usually gets better with antibiotic treatment and rest. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition, but usually involves antibiotics to treat an infection, as well as rest, elevation, and icing of the scrotum.
All A to Z dictionary entries are regularly reviewed by KidsHealth medical experts.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.