- Home
- Parents Home
- Allergy Center
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- A to Z Dictionary
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Food Allergy Center
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Flu Center
- Heart Health
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Diseases & Conditions
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Play & Learn Center
- School & Family Life
- Pregnancy Center
- Newborn Center
- Q&A
- Recipes
- Sports Medicine Center
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Videos
- Para Padres
- Home
- Kids Home
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Movies & More
- Diabetes Center
- Getting Help
- Feelings
- Puberty & Growing Up
- Health Problems of Grown-Ups
- Health Problems
- Homework Center
- How the Body Works
- Illnesses & Injuries
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes & Cooking
- Staying Healthy
- Stay Safe Center
- Relax & Unwind Center
- Q&A
- Heart Center
- Videos
- Staying Safe
- Kids' Medical Dictionary
- Para Niños
- Home
- Teens Home
- Asthma Center
- Be Your Best Self Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Expert Answers (Q&A)
- Flu Center
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Managing Your Medical Care
- Managing Your Weight
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes
- Safety & First Aid
- School & Work
- Sexual Health
- Sports Center
- Stress & Coping Center
- Videos
- Your Body
- Your Mind
- Para Adolescentes
Varicocele
You've heard of varicose veins — those swollen veins that sometimes show up in the legs.
But you might never have heard of a varicocele, which is also a swelling of the veins. A varicocele happens just to guys. That's because it's not in the legs but in a place a bit more private and a lot more tender — the scrotum. It's generally harmless and basically the same kind of thing as varicose veins in the legs.
But what exactly is a varicocele and how do you get rid of it?
What Is a Varicocele?
In all guys, a structure called the spermatic cord (which contains arteries, veins, nerves, and tubes) provides a connection and circulates blood to and from the testicles. Veins carry the blood flowing from the body back toward the heart, and a bunch of valves in the veins keep the blood flowing one way and stop it from flowing backward. In other words, the valves regulate your blood flow and make sure everything is flowing in the right direction.
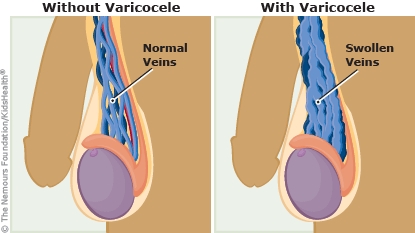
But sometimes these valves can fail. When this happens, some of the blood can flow in reverse. This backed-up blood can collect in pools in the veins, which then causes the veins to stretch and get bigger, or become swollen. This is called a varicocele (pronounced: VAR-uh-ko-seel).
Who Gets Them?
There's no way to prevent a varicocele. They don't happen to every guy, but are fairly common. That's because during puberty, the testicles grow quickly and need more blood delivered to them. If the valves in the veins in the scrotum aren't working as well as they should, the veins can't handle carrying this extra blood. So, although most of the blood continues to flow correctly, some begins to back up, creating a varicocele.
Varicoceles happen mostly on the left side of the scrotum. This is because a guy's body is organized so that blood flow on that side of the scrotum is greater, so varicoceles happen more often in the left testicle than the right. Although it's less common, they can sometimes happen on both sides.
What Are the Signs of a Varicocele?
In most cases, guys have no symptoms at all. A guy might not even be aware that he has a varicocele. When symptoms do happen, it's usually during hot weather, after heavy exercise, or when a guy has been standing or sitting for a long time.
Signs include:
- a dull ache in the testicle(s)
- a feeling of heaviness or dragging in the scrotum
- dilated veins in the scrotum that can be felt (described as feeling like worms or spaghetti)
- discomfort in the testicle or on that particular side of the scrotum
- the testicle is smaller on the side where the dilated veins are (due to difference in blood flow)
How Are Varicoceles Diagnosed?
It's a good idea to get a testicular exam regularly, which is normally part of a guy's regular checkup. Besides visually checking for any unusual lumps or bumps, the health care provider might feel the testicles and the area around them to make sure a guy's equipment is in good shape and there are no problems.
A testicular exam may be done while a guy is standing up so that the scrotum is relaxed. (Some abnormalities like a varicocele can be more easily felt in a standing position.) The doctor checks things like the size, weight, and position of the testicles, and gently rolls each testicle back and forth to feel for lumps or swelling. The doctor also feels for any signs of tenderness along the epididymis, the tube that transports sperm from the testicles.
The spermatic cord is also examined for any sign of swelling. If the doctor thinks there might be a varicocele, he or she might do an ultrasound, which can measure blood flow and identify veins that aren't working correctly.
How Are Varicoceles Treated?
Most varicoceles need no special treatment. A varicocele is usually harmless and more than likely won't affect a guy's ability to father a child later in life.
But if there is any pain and swelling, the doctor may prescribe an anti-inflammatory medicine to relieve it. If the varicocele causes discomfort or aching, wearing snug underwear (like briefs) or a jock strap for support may bring relief.
If the doctor thinks the testicle is being affected by the varicocele or if there's still pain and support doesn't help, a type of surgery called a varicocelectomy may be recommended. This is done by a urologist, a doctor who specializes in urinary and genital problems. The urologist will discuss the different ways a varicocelectomy can be done and recommend the best approach for the patient.
The procedure is usually done on an outpatient basis (meaning there's no need for an overnight hospital stay). The patient usually gets general or local anesthesia. Then, the doctor simply ties off the affected vein to redirect the flow of blood into other normal veins.
In some cases, instead of surgery, doctors can pass a plastic tube into the vein that's causing the varicocele and treat the problem by blocking blood flow to the enlarged vein. Talk with your doctor about whether this treatment might be an option for you.
After surgery, the doctor probably will recommend that a guy wear a scrotal support and use a cold pack on the area to bring down any swelling. There may be discomfort in the testicle for a few weeks, but after that, any aches and pains will go away and everything should be back in full working order.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
