- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
Walking Pneumonia in Kids: Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment
Also called: Atypical Pneumonia
What Is Walking Pneumonia?
Walking pneumonia is a less serious form of the lung infection pneumonia. It's often caused by bacteria called Mycoplasma pneumoniae, but other bacteria or viruses can also cause it.
Most kids with this type of pneumonia (nuh-MOH-nyuh) don't feel sick enough to stay home — hence, the name "walking" pneumonia. But even a child who feels fine should stay home for a few days until antibiotic treatment kicks in and symptoms improve.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Walking Pneumonia?
When it seems like a cold is lasting longer than 7 to 10 days, especially if a cough is getting worse or not going away, it could be walking pneumonia. Symptoms can come on suddenly or take longer to start. The symptoms are often mild, but sometimes can be more severe.
Walking pneumonia symptoms to look for:
- a fever of 101°F (38.5°C) or below
- a cough that can last for weeks to months
- fatigue (feeling very tired)
- headache, chills, sore throat, and other cold or flu-like symptoms
- ear pain
- chest pain or stomach pain
- malaise (feeling of discomfort)
- vomiting
- loss of appetite (in older kids) or poor feeding (in infants)
- rash
- joint pain
- fast breathing or breathing with grunting or wheezing sounds
- retractions, which are a sign that someone is working hard to breathe. The areas below the ribs, between the ribs, and in the neck sink in with each attempt to inhale.
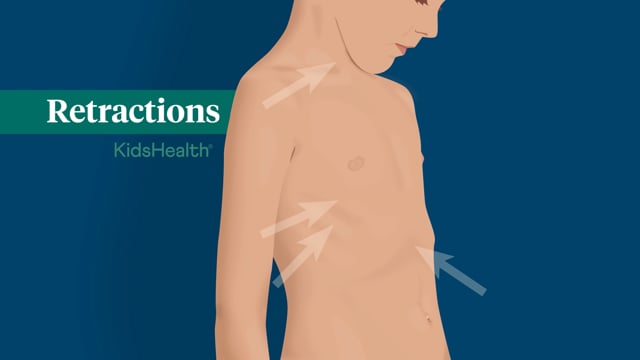
Retractions
Walking pneumonia symptoms usually depend on where the infection is concentrated. A child whose infection is in the top or middle part of the lungs will probably have labored breathing. Another whose infection is in the lower part of the lungs (near the belly) may have no breathing problems, but may have an upset stomach, nausea, or vomiting.
How Is Walking Pneumonia Diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose walking pneumonia by doing an exam. They'll check a child's breathing and listen for a crackling sound that often indicates walking pneumonia.
If needed, they might order a chest X-ray or tests of mucus samples from the child's throat or nose to confirm the diagnosis.
How Is Walking Pneumonia Treated?
Antibiotics are an effective treatment for walking pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. A 5- to 10-day course of oral antibiotics is usually recommended. If your doctor prescribes antibiotics, make sure your child takes them on schedule for as long as directed to recover more quickly.
After starting on antibiotics, your child is less likely to pass the illness to other family members. But encourage everyone in your household to wash their hands well and often. Don't let your child share drinking glasses, eating utensils, towels, or toothbrushes.
Teach kids to cough or sneeze into a tissue or into their elbow or upper arm (not their hands). Wash your hands after touching any used tissues. Also make sure that your kids are up to date on their vaccines to help protect them from other infections.
How Can I Help My Child Feel Better?
Your child should drink liquids throughout the day, especially if they have a fever. Ask the doctor before you use a medicine to treat a cough. Cough suppressants stop the lungs from clearing mucus, which might not be helpful for lung infections like walking pneumonia.
For a fever or chest pain, acetaminophen (such as Tylenol or a store brand) or ibuprofen (such as Advil, Motrin, or a store brand) can help make your child more comfortable. Do not give aspirin to your child or teen as it's linked to a rare but serious illness called Reye syndrome, which can lead to liver failure and death.
With treatment, most types of bacterial pneumonia go away within 1–2 weeks. Coughing can take up to 4–6 weeks to stop.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
