- Home
- Parents Home
- Allergy Center
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Food Allergy Center
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Flu Center
- Heart Health
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Diseases & Conditions
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Play & Learn Center
- School & Family Life
- Pregnancy Center
- Newborn Center
- Q&A
- Recipes
- Sports Medicine Center
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Videos
- Para Padres
- Home
- Kids Home
- Asthma Center
- Cancer Center
- Movies & More
- Diabetes Center
- Getting Help
- Feelings
- Puberty & Growing Up
- Health Problems of Grown-Ups
- Health Problems
- Homework Center
- How the Body Works
- Illnesses & Injuries
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes & Cooking
- Staying Healthy
- Stay Safe Center
- Relax & Unwind Center
- Q&A
- Heart Center
- Videos
- Staying Safe
- Kids' Medical Dictionary
- Para Niños
- Home
- Teens Home
- Asthma Center
- Be Your Best Self Center
- Cancer Center
- Diabetes Center
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Expert Answers (Q&A)
- Flu Center
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Managing Your Medical Care
- Managing Your Weight
- Nutrition & Fitness Center
- Recipes
- Safety & First Aid
- School & Work
- Sports Center
- Stress & Coping Center
- Videos
- Your Body
- Your Mind
- Para Adolescentes
Fever (High Temperature) In Kids
All kids get a fever from time to time. Usually, a fever isn’t dangerous or bad for kids. It can even be a good thing because it can help the immune system fight infection.
Still, parents might be unsure about how to handle a fever at home and when to call the doctor. Here are some tips.
What Is a Fever (High Temperature)?
In general, a fever means the body’s temperature is 100.4°F (38°C) or higher. Different ways of measuring a temperature — rectal, armpit, ear, forehead, or mouth — get a slightly different number, so the number that means a child has a fever is a little different too.
What Causes Fever (High Temperature)?
Fevers in kids are usually caused by an infection. A fever helps the body by stimulating the immune system to fight the infection. Doctors also think the higher temperature makes it harder for the germs to grow.
A few other reasons kids can have a fever:
Overdressing: Infants, especially newborns, may get fevers if they're overdressed, wrapped in a blanket, or in a hot environment because they don't regulate their body temperature as well as older kids. But because fevers in newborns can be a sign of a serious infection, even infants who are overdressed must be checked by a doctor if they have a fever.
Immunizations: Babies and kids sometimes get a mild fever that lasts about a day after getting vaccinated.
A child who is teething might have a slight rise in body temperature, but it's probably not the cause if the temperature is higher than 100°F (37.8°C).
When Is a Fever (High Temperature) a Sign of Something Serious?
In most healthy kids who are acting well, a fever isn’t serious.
Serious fever symptoms to watch for:
- Infants younger than 3 months: If an infant younger than 3 months has a rectal temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, call your doctor or go to the ER right away.
- Kids with some health conditions: If your child has an ongoing health issue, make sure you know if the doctor should be called for fever.
A fever probably is not serious if your child is 3 months or older and:
- is still interested in playing
- is drinking well
- is alert and smiling
- has a normal skin color
- looks well when their temperature comes down
Don't worry too much about a child with a fever who doesn't want to eat. This is common with infections that cause fever. For kids who still drink and urinate (pee) normally, not eating as much as usual is OK.
What Are the Signs of a Fever (High Temperature)?
Fever symptoms to watch for in kids:
- feeling warm
- acting differently (they might be fussy or cranky, or quieter than usual)
- breathing a little faster or have a faster heart rate than normal
- having a headache
- having chills or sweating
- having red or flushed skin
For any of these signs, take your child’s temperature to know if they really have a fever.
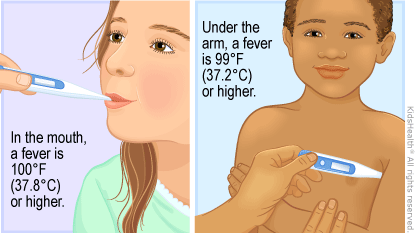
How Should I Take My Child's Temperature?
If your child feels warm or is acting unwell, use a digital thermometer to confirm a fever. Different ways of taking the temperature are more accurate than others at measuring the true body temperature.
The best way to take a temperature:
- for kids 3 years old and younger: a rectal temperature
- for kids 4 or older who can cooperate: an oral temperature (by mouth)
- for any age: under the armpit (axillary) and temporal artery (forehead) are easiest but less accurate. Tympanic (in the ear) is OK for kids 6 months and older.
It's a fever when a child's temperature is at or above one of these levels:
- rectal (in the bottom), tympanic (in the ear), or temporal artery (across the forehead): 100.4°F (38°C)
- oral (in the mouth): 100°F (37.8°C)
- axillary (under the arm): 99°F (37.2°C)
Treating a Fever (High Temperature): How Can I Help My Child Feel Better?
No treatment is needed if a child is still playing and drinking normally and doesn’t have pain.
Treating a fever with medicine isn't needed if a child is still playing and drinking normally and doesn’t have pain. Give medicine only when a fever causes a child discomfort or keeps them from drinking.
While kids have a fever, keep an eye on them, help them to rest, and keep offering liquids to drink. They need to drink a little extra to make up for the fluids they lose from sweating.
Fever (High Temperature): Home Care Measures
Medicines
If your child is uncomfortable from a fever or not drinking liquids well, you can give one of these medicines:
- acetaminophen (such as Tylenol or a store brand)
or - ibuprofen (such as Advil, Motrin, or a store brand). Do not give to children under 6 months old.
Follow the package directions for how much to give and how often. If you don't know the recommended dose or your child is younger than 2 years old, call the doctor to find out what to use and how much to give.
- If your child has any medical problems, check with the doctor to see which medicine to use.
- Unless instructed to by a doctor, never give aspirin to a child. Such use is linked to Reye syndrome, a rare but serious illness.
Do not give any medicine for fever to infants younger than 3 months old unless instructed to by a doctor.
Staying Comfortable
If your child has a fever:
- Have them wear lightweight clothing and stay covered with a light sheet or blanket. Heavy clothes and blankets can keep the body from cooling, which can make your child uncomfortable.
- Keep the room at a comfortable temperature — not too hot or too cold.
- Make sure they get plenty of rest. Staying in bed all day isn't necessary, but a sick child should take it easy.
- They should stay home from school or childcare until their temperature has been normal for 24 hours.
Lukewarm sponge baths to lower a fever generally are not recommended. In fact, sponge baths can make kids uncomfortable from shivering. Never use rubbing alcohol (it can cause poisoning when absorbed through the skin) or ice packs/cold baths (they can cause chills that can raise body temperature).
Food and Drinks
Offer plenty of liquids to avoid dehydration because fevers make kids lose fluids faster than usual. Oral rehydration solutions (like Pedialyle, Enfalyte, or store brands) are a good choice. You also can give water, soup, ice pops, and flavored gelatin. Avoid drinks with caffeine, including colas and tea, which can make dehydration worse by making kids pee more often.
Let kids eat what they want (in reasonable amounts), but don't force it if they don't feel like eating much.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
The temperature that should trigger a call to the doctor depends on a child's age, the illness, and whether they have other symptoms. You might ask if your doctor has specific guidelines on when to call about a fever.
In general, call the doctor if your child is:
- younger than 3 months old with a rectal temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- 3 months or older with a temperature higher than 102.2°F (39°C)
- any age but has a health problem like cancer or sickle cell disease and has a fever
Also call the doctor if your child is 3 months or older, has a fever, and:
- doesn't want to drink liquids or seems too ill to drink enough
- has lasting diarrhea or repeated vomiting
- has any signs of dehydration (peeing less than usual, not having tears when crying, less alert and less active than usual)
- has a specific complaint (like a sore throat or earache)
- still has a fever after 2–3 days
- has a rash
- has pain while peeing
Get emergency care if your child shows any of these signs:
- crying that won't stop
- extreme irritability or fussiness
- sluggishness and trouble waking up
- a rash or purple spots that look like bruises on the skin (that were not there before your child got sick)
- blue lips, tongue, or nails
- in an infant, the soft spot on the head seems to be bulging out or sunken in
- stiff neck
- severe headache
- limpness or refusal to move
- trouble breathing that doesn't get better when the nose is cleared
- leaning forward and drooling
- seizure
- moderate to severe belly pain
What Else Should I Know?
All kids get fevers, and in most cases they're back to normal within a few days. For older babies and kids, the way they act can be more important than the reading on your thermometer. Everyone gets a little cranky when they have a fever. This is normal and should be expected.
But you know your child best. If you're ever in doubt about what to do or what a fever might mean, or if your child seems ill in a way that concerns you even with no fever, always call your doctor for advice.
Taking Your Child’s Temperature
Your child feels warm, but is it a fever? Now, more than never, it’s important to know. Here's how to use a thermometer to get an accurate reading at every age.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.

