- Home
- Humana Medicaid
- Kentucky Medicaid
- Medicaid extras
- Health and wellness
- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
When Is an Illness Contagious?
When an illness is contagious, it means you can catch it from another person. How do you know when an illness is in the contagious stage? Most viral illnesses are contagious before any symptoms start. So an infected person can spread a virus before feeling sick. This makes it almost impossible to stop the spread of infections.
Contagious diseases (such as the flu, colds, or strep throat) spread in several ways, such as through direct physical contact, like touching or kissing a person who has the infection. Another way is when an infectious germ travels through the air after someone nearby sneezes or coughs.
Some childhood rashes — such as hand, foot, and mouth disease, chickenpox, and ringworm — spread through skin-to-skin contact. So kids with a rash should avoid contact with others until the spots crust over.
The best way to fight germs and keep them from spreading is to make sure that kids (and adults!) wash their hands well and often, especially:
- after playing outside
- before eating
- after going to the bathroom
- after coughing or sneezing
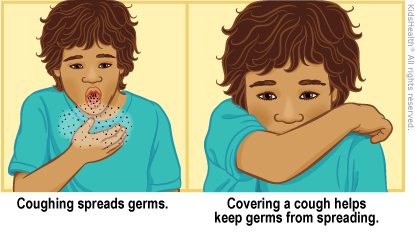
Also, teach the kids to cover their coughs and sneezes. If they don't have a tissue handy, they should cough or sneeze into an elbow, not their hands.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.