- Parents Home
- Para Padres
- A to Z Dictionary
- Allergy Center
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Emotions & Behavior
- First Aid & Safety
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergies
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Heart Health & Conditions
- Homework Help Center
- Infections
- Newborn Care
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Play & Learn
- Pregnancy Center
- Preventing Premature Birth
- Q&A
- School & Family Life
- Sports Medicine
- Teens Home
- Para Adolescentes
- Asthma
- Be Your Best Self
- Body & Skin Care
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Diseases & Conditions
- Drugs & Alcohol
- Flu (Influenza)
- Homework Help
- Infections
- Managing Your Weight
- Medical Care 101
- Mental Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Q&A
- Safety & First Aid
- School, Jobs, & Friends
- Sexual Health
- Sports Medicine
- Stress & Coping
A to Z: Cystitis
Cystitis (sis-TYE-tis) is inflammation of the bladder, also known as a bladder infection. It's the most common type of urinary tract infection (UTI) and mostly affects children and adult women.
More to Know
Cystitis is usually caused by bacteria (typically E. coli) that enter the body through the urethra and spread to the bladder. If not treated, the infection can travel to the kidneys and become a more serious problem.
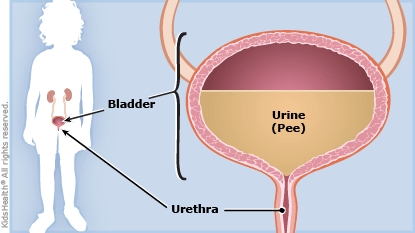
Cystitis can occur in people who are otherwise healthy and have no medical problems. Irritants such as bubble baths or feminine hygiene products, poor toilet or hygiene habits, an abnormality in the structure or function of the urinary tract, drug interactions, or long-term catheter use all can cause a bladder infection.
Symptoms of cystitis include a persistent urge to urinate (pee), a burning sensation when urinating, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, low-grade fever, and a feeling of pressure or pain in the lower abdomen.
Wetting accidents in toilet-trained children often indicate cystitis. For infants and young children, cystitis may be harder to detect because symptoms are less specific. Sometimes fever is the only sign.
Keep in Mind
Bladder infections are painful and inconvenient, but most are caused by bacteria and can easily be treated with antibiotics. If you have blood in your urine, pain with urination, back or side pain, fever, nausea or vomiting, or abdominal pain, see your doctor immediately as these are signs of a possible infection in the urinary tract.
All A to Z dictionary entries are regularly reviewed by KidsHealth medical experts.

© 1995- The Nemours Foundation. KidsHealth® is a registered trademark of The Nemours Foundation. All rights reserved.
Images sourced by The Nemours Foundation and Getty Images.
